
Sign up to receive latest insights & updates in technology, AI & data analytics, data science, & innovations from Polestar Analytics.
Editor’s Note: From port congestion, spillover impacts from geopolitical conflicts, and freight transportation issues and more manufacturing and supply chain has become more challenging (like it wasn’t before) in the past few years. Understand impact of analytics in manufacturing specially for supply chain processes with these use cases.
For any successful manufacturing firm, it is very important to find a new way to streamline its operations. Starting from the raw materials to WIPs, logistics and of course, the final product, manufacturing is an intricate process with countless moving parts. For example, an average car engine would have more than 2000 individual components – think about the scale to extrapolate it for multiple vehicles and functions.
Besides the tangible aspects of the manufacturing industry, there are financial and managerial aspects to oversee, not to mention a perpetually changing market demand and aggressive competition.
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a lot of automation, cost pressure is always high and the margins thin. Bringing in efficiency and productivity gain is important to ensure you are competitive as well as profitable. Hence analysing different moving parts spread across functions to make sure they seamlessly work in tandem to bring down the cost, push up the utilization, and increase the margins.
Discover how to revolutionize your production processes with winning strategies tailored to your business needs.
Get in TouchIt takes months and extreme due diligence in examining each stage, coming up with innovative ideas and finally implementing them. The recent technological disruptions are not only good for manufacturers’ internal processes but are also a way to remain competitive and achieving organisation goals.
A World Economic Forum (WEF) and A.T. Kearney’s study of the future of production find that manufacturers are evaluating how combining emerging technologies including IoT, AI, and machine learning can improve asset tracking accuracy, supply chain visibility, and inventory optimization.
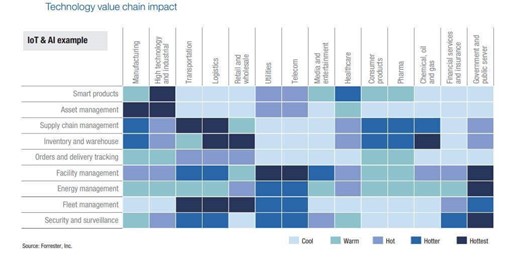
Source: WEF & A.T. Kearney Report
But, how can these organisations improve their underlying manufacturing processes and practices and practices before the enterprise-wide tech adoption?
There are a series of processes going on in parallel and it generates a huge volume of data ranging from machine run-time to no. of units produced. When all this information is decoupled, analyzed, and resynched together in a system, the results can be very powerful.
Machinery and systems are constantly operating for long stretches under heavy loads and any fault can significantly impact your production. As a reactive approach is not sustainable, by using predictive analytics systems, factory supervisors can predict failures in advance and avoid downtime. A practice that is catching trend is self-correcting machines that warn once such a threshold is achieved.
Machine utilisation and effectiveness data can lead to some crucial insights like
These can show benefit by reducing the maintenance costs, improve machine efficiency, reliability and more. It is estimated that Predictive maintenance has the potential to reduce maintenance costs by 19%.
In addition to the manufacturing production line, the use of analytics is often limited to warehouse optimization and forward logistics. However, while performing Reverse Logistics Analytics on numerous occasions organisations have dug up some hidden insights into sunk costs and inefficiencies cropping up from certain activities.
Learn how powerful visualization and data analytics can help optimize your processes right from raw material sourcing to final product delivery.
Get Your Free CopyAnalysis of returned items provide insights related to which stage of the production process is generating the maximum volume of faulty pieces or end products. It leads to avoiding loss emanating due to customers dissatisfaction as well as the sunk cost associated with manufacturing them. Further, it also adds to optimizing the existing processes, updating the vendor scorecard and ratings.
Advanced data analytics in manufacturing maximizes operational efficiency through three key applications: Predictive Asset Maintenance, Yield/throughput analysis and Supply chain optimization with advanced modelling.
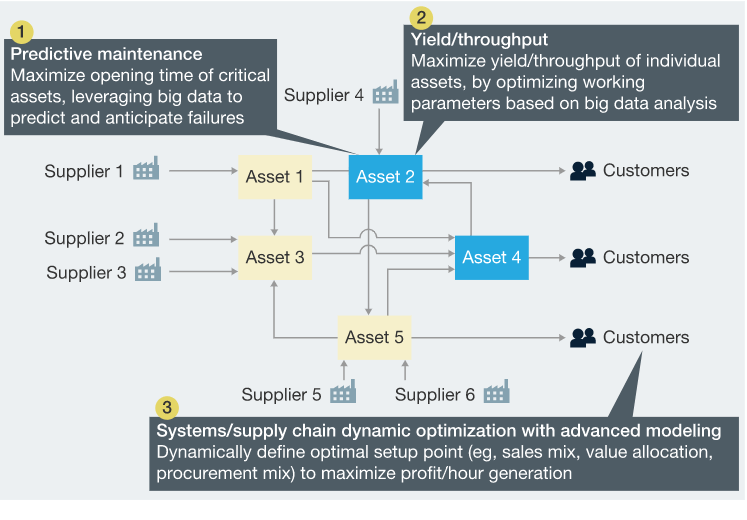
There are several areas of supply chain management where data analytics can be of significant help.
Now, Suppliers & Manufacturers have a choice to share their production data with their partners and customers to bring in transparency and gain trust. This way the manufacturer can see exactly whether the supplier is delayed with production just in time to avoid any additional lead time. At the same time, the suppliers can pre-empt any such incident and modify their production output accordingly.
A report by World Economic Forum, estimates the potential value of data sharing to be over $100 billion, by focusing on manufacturing process optimization based on best practices. The top 5 application domains include: Enhancing asset optimization, tracking products across value chain, tracing process conditions, exchanging digital product characteristics, and verifying provenance.
With greater visibility into supplier quality levels and their other performance metrics, manufacturers can:
Though supplier management is a vital part of any supply chain analytics solution there are a lot of KPIs that can be tracked, if interested you can find more procurement KPIs here.
Having supplier production and quality information available can also provide all the insight needed for better risk management. Supplier dependencies are quantifiable and with timely analysis of this information, the manufacturer can make fact-based decisions for Strategic Risk Management. Take a look at what have had the most impact on manufacturer’s supply chains:
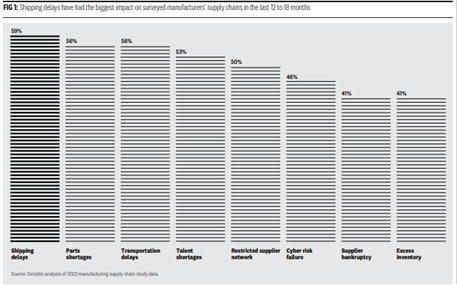
Source: Delloite
Mapping such delays to your supply chain and working on the controllable actions like shortages, restricted supply chain networks, excess inventories, etc. can tie combine data analytics and manufacturing operations efficiencies.
Manufacturers not only create products for their current customers only, but also for the perceived demand that they expect to emerge soon. Demand forecasting is key because it suggests an optimum capacity for a production chain and that can be the difference between strong sales or a warehouse full of unpurchased inventory.
Traditionally, forecasts are based on previous years’ historic values, and not on more actionable forward-looking data. By combining existing data with predictive analytics in manufacturing to build a more precise projection of what purchasing trends, seasonality, fads and disruptions could be, they can gain significant competitive advantage.
Additionally with demand forecasting as input, organizations can perform demand planning by incorporating the market and competition data as well as how well the production lines are operating i.e. by unconstrained and constrained demand, leading to better sales and operations planning, smarter risk management and lesser cost emerging due to access inventory storage space.
Demand planning and Demand forecasting are like the Yin-yang of S&OP one is the input for the other. Though demand planning remains at the top of the list, supply chain leaders are already trying to use other AI use cases in manufacturing, few of them include:
In addition to these manufacturing analytics examples, some other use cases include:
- Capacity Planning: To define the capacity and optimal units of the goods to manufacture for each production cycle, based on technology and human capital for a specific period. Considerations: capacity, sales forecasts, and parallel schedules.
- New Product demand: Forecast potential demand for new products based on market research and historical data and mitigate risks beforehand.
- Pricing and Promotion strategies: To create informed pricing strategies by understanding market demand, competitor pricing or real-time demand fluctuations.
Roping in the daily manufacturing data, the BI analytics dashboards can project a clear picture of the actual number of units manufactured over-reporting month in each production unit, making it easy for stakeholders to streamline the workflow and concentrate on the required areas.
With ever-growing SKUs, a limited shelf space, massive competitions, and thin margins manufacturers are always faced with pressure. This means that they have to ensure they have the right inventory at multiple levels right from warehouses to the retail shelfs. We’ve previously spoken about how sharing data can create more value synergy – this applies to inventory too as tracking products across value chain can lead to a potential gain of ~ $40 billion.
Additionally, it can help create true end-to-end visibility and bring more transparency. Depending on the number of companies participating you can create new inventory models upon which analytics can be done easily.
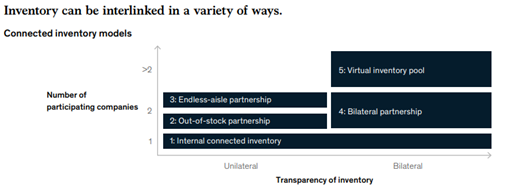
A few types of diagnostic inventory analytics techniques in manufacturing include:
Additionally, manufacturers can leverage supply chain predictive analytics use cases like Collaborative Filtering, Causal Inference, Scenario Planning, Neural Networks, multi-variate regression models, demand shaping techniques, and exponential smoothing for short-term forecasting to find inferences and forecast data for the future.
Manufacturers must deal with a number of vendors and distribution partners to procure or distribute different parts or finished goods. It is very important to keep a check on the associated costs and the profitability numbers. Having a cost analysis solution that integrates all the information on a single platform and allows you to get actionable insights, can really bring efficiencies across these activities.
There are a lot of associated costs when manufacturers deal with vendors and distribution partners to procure or distribute different parts or finished goods. It is very important to keep a check on these costs and the profitability numbers.
Having a cost and spend analysis solution that integrates all the information on a single platform and allows you to get actionable insights, can really bring efficiencies across these activities.
Keeping track on the cost per unit of the item is important for a production manager as it impacts the pricing decisions and promotions as well. Calculating it requires data on costs like:
Having a BI solution for reporting and visualisation can significantly reduce the risk and suggest timely corrections.
The excessive Overhead costs could be detrimental to manufacturing profitability. To have real control and visibility over these costs, connected data sources and advanced analytics capabilities are needed. Labor cost forms a major chunk of overhead costs. Hence, it is critical to link not only job roles and wages to certain processes but individuals. Employee badges can be tracked with sensors placed on the shop floor. This data can be analysed to assign the exact cost of each task in a process, broken down to an individual’s level. We are observing a growing adoption of these smart IoT devices in the factories.
At Polestar Analytics, we help companies in becoming a connected enterprise where the data sources are connected and everyone in the company has access to the right data, at the right time to achieve operational efficiencies.
If you are looking for a data analytics partner in India or an offshore engagement, our data science teams can help you set up a robust data management and analytics platform. Why not today and let’s get started?
About Author

Assistant Vice President
You can't hire somebody else to do your pushups for you.