
Sign up to receive latest insights & updates in technology, AI & data analytics, data science, & innovations from Polestar Analytics.
Have you returned a good or item that you have ordered this week or month? If you buy goods online, your answer might have been yes. With research stating “96% of customers who are satisfied with the returns process said that they’ll purchase with the Retailer again”, Hassle-free returns have become a requirement for firms. But have you thought about how companies manage the return of goods? This would broadly come under the reverse logistics management of the company.
Before we delve into the details, let’s have a refresher on what the types of logistics are. And also how reverse logistics and traditional logistics differ.
Logistics or Logistics Management is a part of Supply Chain Management that refers to the process of managing, transportation, and storage of resources or goods (or services or information) and their flow between the point of origin and point of consumption. For now, think about what the final point of consumption would be. We’ll talk about this later.
Logistics is divided into many types, but broadly speaking there are two major bases of divisions. One, is based on the type of resources in and out of Manufacturing i.e. Inbound and Outbound logistics.
Second, is based on the flow of goods from the POV of the Customer, namely Forward and Reverse Logistics.
Reverse Logistics deals with bringing the product a step back in the traditional value chain or supply chain. For example, defective goods coming back from the retailer to the Wholesaler. Another form might be moving the final product after consumption for disposal or using it to form Raw material for the same or a completely different product, which can take place anywhere in the Inbound and Outbound Logistics cycle.
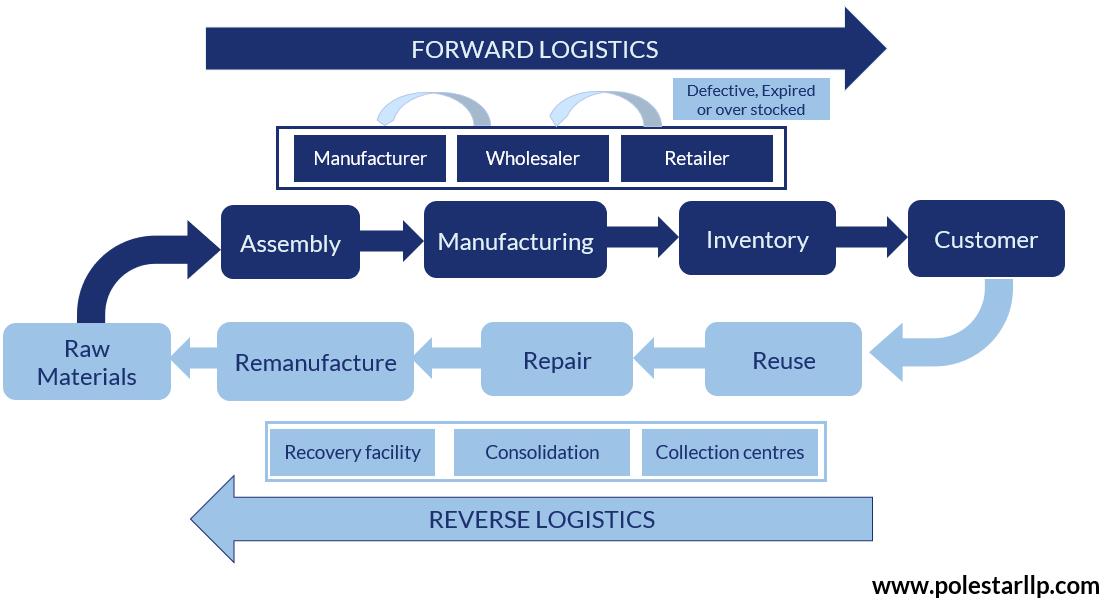
We asked you to think about who the end customer would be, remember? For example, the water bottle or cold drink that you drink, are you the end customer? Probably not. The bottles are collected, consolidated, and sent to recovery facilities where they can be broken down into bits and used again for the manufacture of plastic or for the construction of roads, etc. Making either the manufacturer or the disposal unit the end consumer.
The five Rs of reverse logistics are returns, reselling, repairs, repackaging, and recycling. It is these 5R’s that can help you streamline your logistics and reduce losses.

From the point of return by the consumer in Retail to the re-use of materials, understanding the value chain of industries and linking one to the other is of important. With value mapping, one can reduce the costs associated with reverse logistics and can still produce value from goods after it is consumed by the designated end-consumer.
Think of the horticulture sector, the flowers that can be used in weddings or functions, with efficient reverse logistics can be useful in the perfume or potpourri industry, by re-selling the used flowers. Another real-world implementation concerning Reselling and Recycling is that of Levi Strauss, who partnered with Blue Jeans Go Green in the U.S. and Canada, and other organizations in different countries to collect used clothing and use them in the production of new Jeans or use them as Authorized Vintage.
You might be thinking, why are we talking about all this? Take the Retail Sector, it is estimated that in brick and mortar stores the returns percentage would be 8-10% and 20-30% in E-commerce. Returns have been emerging as a key factor for Customer Retention. According to a Consumer Study, concerns with Return Policy consist of 60% of the Top 5 reasons.
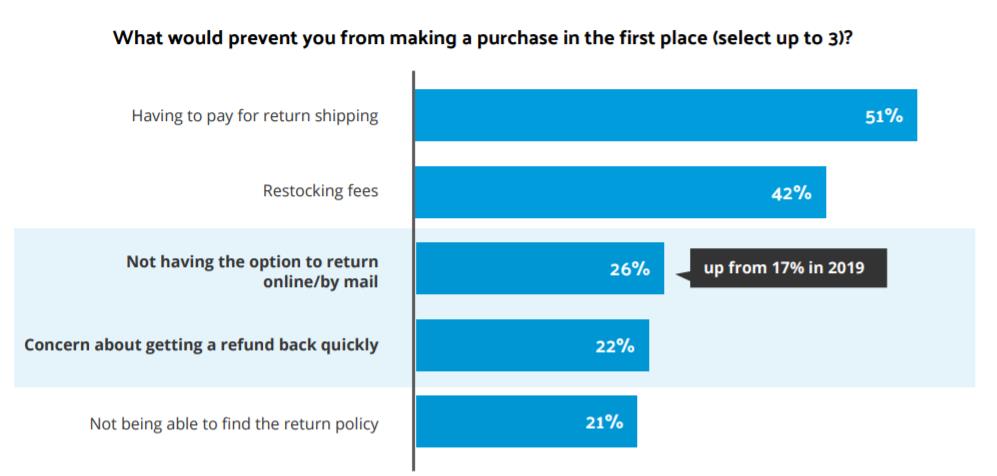
Returns are worth almost a trillion dollars annually. But for most organizations, Reverse Logistics is a cost center. Some companies keep stocking the returned items causing an increase in Warehouse cost and for others, it takes a considerable financial strain on the supply chain to reach out to the Consumers. For example, Walmart, Target, and Amazon sometimes refund the money and tell customers to skip returning an item. The added risk of cross-contamination between the goods, in case of personal items like Hygiene products.
Construction Industry
Recyclable items can be moved to different sites or used on the same site for further construction. With the industry moving towards sustainable practices like the use of plastic etc. in the construction of roads for increasing the durability and also requirements of the Green Building like usage of broken bricks etc for soil filling.
Food and Beverages Industry
With organizations moving towards Zero waste, they have been trying to produce lesser plastic to reduce wastage. Also in a few places of Africa, plastic bottles and their caps are being used to construct homes.
Technology Industry
Companies like Cisco, have incorporated reduction of packing material, virgin plastics in their CSR Activities, and also reducing the waste they produce and diverting the waste we do generate through recycling, composting, and donations.
Till now we have seen some of the major players in the industry move towards improving their reverse logistics. Some for the environment even with a strain on their finances, while others take it as an opportunity to maintain an efficient flow of goods throughout.
Gartner’s survey shows that 70% of Supply Chain Leaders plan to invest in a Circular Economy, which would optimize the ecosystem of waste materials. As such, implementing sustainable practices and creating value from material rendered as waste can be seen. An “Optimized” set of Reverse logistics practices and processes have benefits like:
There might be technical difficulties or a lack of infrastructure for optimizing your processes. But Analytics can help you leverage the data collected to improve your bottom line. Logistics analytics solutions can aid in several use cases within reverse logistics, enhancing efficiency and decision-making processes.
If you’re from a Retail firm, are you analyzing why your customers return goods? And in which category is the returns being generated in a higher percentage? Even though we speak a lot about reuse, recycling, and reselling if we can reduce the returns the impact would be obvious on the top and the bottom line. For example, looking at the major reasons for return can help firms reduce wastage.
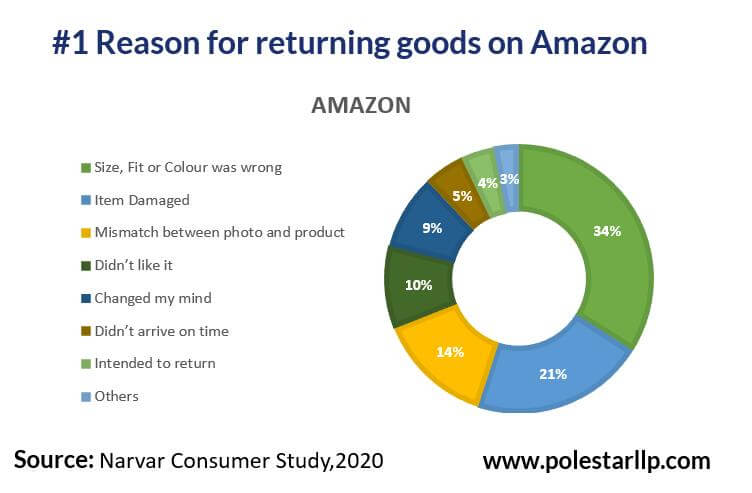
Given these insights, for e-retailers mismatch between photo and product can be a target place for elimination of wastage along with the Size and Fit. These can be eliminated with better quality checks for the representation of products and wouldn’t require much infrastructure. For manufacturers, the number of defective items raises questions about the %wastage and how effectively it is moving towards Lean Manufacturing or Lean Six Sigma.
The type of returns can also influence the future course of the product. For example, excess goods and eligible returns are donated by Amazon with - “Fulfilled by Donation” with sellers’ collaboration. This would help in both CSR activities and reduce the Warehouse charges. And items like defective goods can be disposed of instead of being stored. In any way, with data, the potential of the goods can be identified for its future course.
The problem of reverse logistics is not just limited to Retail, most of the industries have issues somewhere or the other. By the integration of Inbound and Outbound logistics, we can eliminate defective suppliers by linking raw materials to the finished goods and the customer order. But this would require a Connected Planning approach or robust Business Intelligence or Visualization tools. This interlinking can help you identify any faulty goods and help issue recalls early in the value chain.
Ask yourself questions like - Is the logistics optimized? Are you picking up returns while delivering or are the empty pallets and full pallets being picked up and dropped while optimizing the routes? And so on. All these can be analyzed with your logistics and transportation routes and to identify the most optimal path.
Okay, this term is a little broad, but there are a plethora of scenarios that one can think of. Have you thought of changing the packing material for reduction of impact on the environment but how would it play on the financial planning? Use Anaplan for Scenario planning of the same. Not only these but want to partner with a Returns store or want an M&A with a Returns store, where consumers can drop off their returned goods (Like the Amazon-Kohl Partnership or the Happy Returns Store), make plans for knowing what the impact of the decisions you have taken or want to take would be.
The future will be about minimizing the disruptions from returns as well as keeping in check the environmental footprint left by companies. The future of reverse logistics involves using integrated supply chain management software that would help make these connections and can also provide valuable reports. This would be especially important with increasing production and volume of returns y-o-y. With integrated software companies can ensure a seamless forward and reverse logistics process.
Instead of treating reverse logistics as a cost center, minimize waste and optimize planning. Use the 5Rs to have a positive impact on your bottom line and for the environment to move towards sustainable planning. Let Polestar Analytics help you in this journey by bringing out insights from your data that would alter the way you operate.
About Author

Data & BI Addict
When you theorize before data - Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts.