
Sign up to receive latest insights & updates in technology, AI & data analytics, data science, & innovations from Polestar Analytics.
Editor’s Note: Dive into the world of Enterprise Data Management (EDM) in our comprehensive article. Explore key pillars, data maturity curves, and create an EDM strategy. Uncover essential components for data governance, integration, security, and utilization. Discover the three-layered approach and assess your organization's Data Maturity Curve. Learn best practices and functions of an efficient Enterprise Management Software system. Don't miss this ultimate roundup on Enterprise Data Management!
After hearing the term “Enterprise data management”, you might get confused with it with Master Data Management.
We understand that both terms are an integral part of effective data management, but they possess distinct focuses and objectives.
Master Data Management (MDM) is a specialized field in data management that focuses on managing organization's crucial data elements known as master data. Master data encompasses fundamental business entities like customers, products, suppliers, employees, and other significant entities shared across different systems and applications. The primary goal of MDM is to establish and maintain a unified, trustworthy, and authoritative source of master data that can be consistently utilized throughout the enterprise.
Key to a successful master data management.
Explore NowOn the other hand, Enterprise data management is a broader discipline that includes a range of tasks, including data governance, data quality management, data integration, data security, and data architecture. The aim is to ensure the accuracy, consistency, security, and availability of data for authorized users when required.
In shorter terms, it’s "An organization's ability to specify, incorporate, retrieve, and store data for both internal processes and applications, as well as external communications."
Within an organization, Enterprise Data Management (EDM) employs a set of processes, practices, and technologies to ensure that all types of data are:
Before diving into identifying different pillars, layers, software, and strategies of Enterprise Data Management, let's first examine the different types of data within an enterprise.
1. Master Data – It encompasses standardized identifiers that describe non-transactional information about core business objects. Refers to unique entities in domains like Products, Customers, Vendors, etc. For example, a vendor with standardized properties serves as master data, identified by a unique ID used in transactional systems for business activities.
2. Transactional Data – focuses on specifics of core business activities and transactions. It encompasses information related to procurement, production, sales, and other operational activities. An example of transactional data is the detailed description of a product sale.
3. Analytical Data– Analytical or reporting data refers to aggregated and consolidated information derived from transactional data. It allows for comprehensive analysis of business activities by utilizing master data to segment and analyse the data from different perspectives.
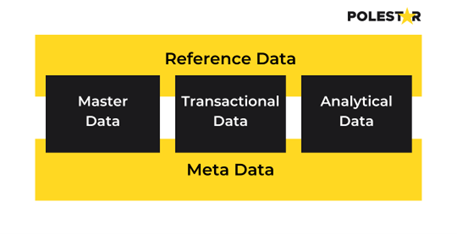
4. Reference Data– It is a subset of master data that maintains consistent standards and is less prone to frequent changes. It serves as a standardized point of reference throughout the organization. For instance, a list of countries, states, and cities is an example of reference data that provides a common framework for maintaining uniformity.
5. Meta Data– It offers descriptive and structural details about other data that pertains to business activities. For instance, the name of a person may consist of three components: First Name (mandatory), Last Name (mandatory), and Middle Name (optional). This information serves as metadata providing additional context about the structure and components of a person's name.
Incorporating these diverse data types, Enterprise data management operates through a well-structured and interconnected three-layered approach. Let’s have a look:
First Layer: Data
The data layer forms the foundation of EDM and encompasses activities related to data capture, storage, organization, and quality. It involves processes such as data acquisition, data cleansing, data integration, and data governance. The data layer ensures that accurate, consistent, and reliable data is available for analysis and decision-making.
Second Layer: Visualization
The visualization layer focuses on presenting data in a meaningful and easily understandable way. It involves the use of data visualization techniques, such as charts, graphs, dashboards, and reports, to convey insights and patterns hidden within the data.
Third Layer: Integration
The integration layer involves integrating data from various sources and systems to create a unified and comprehensive view of information across the organization. It includes processes like data integration, data migration, and data synchronization. This layer ensures that data flows seamlessly between different systems and applications, enabling efficient data exchange and collaboration.
Together, these three layers work cohesively to ensure that data is effectively managed, visually represented for better understanding, and integrated to support the organization's data-driven needs. They enable organizations to harness the full potential of their data, enhance decision-making processes, and drive business success. As we know all too well, data integration is more than just plugging in new technology to your stack.
Have a look into the key pillars of a successful data integration strategy for enterprises
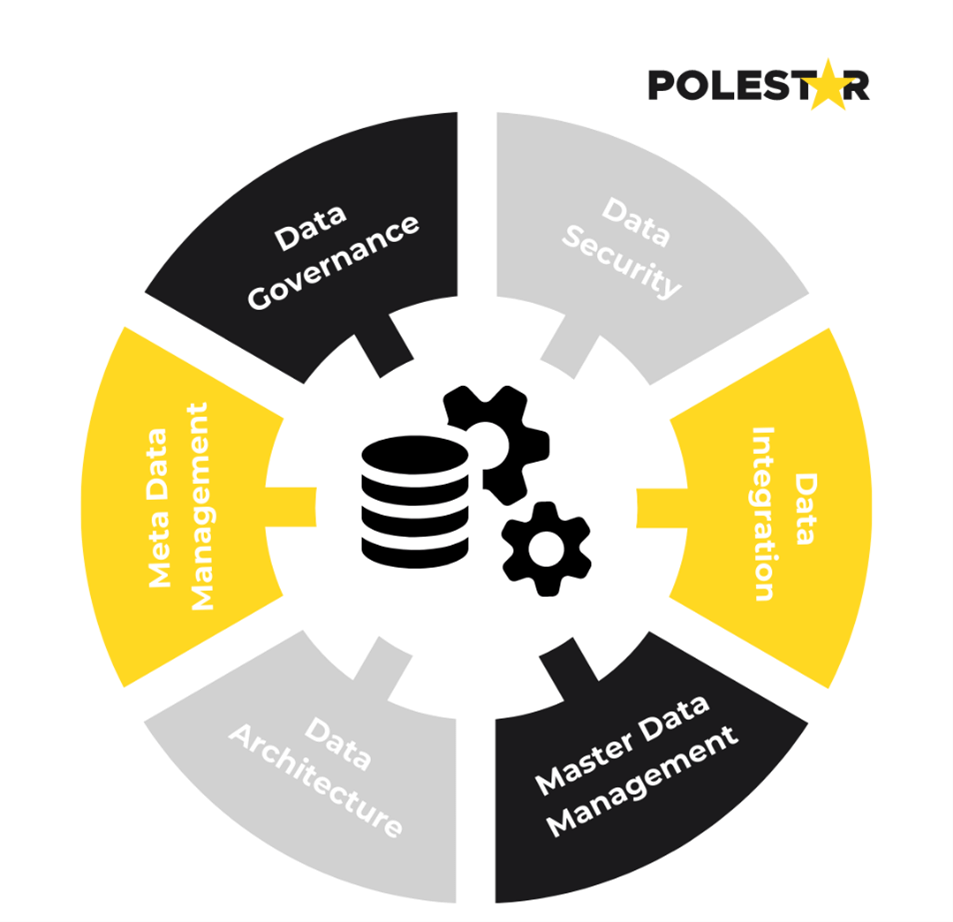
A company's Enterprise Data Management (EDM) system consists of six core components that fulfill specific roles in data management. It includes:
1. Data Governance – policies, processes, and procedures for managing and ensuring the quality, integrity, and security of data.
2. Data Security– implementing measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, modification, or disclosure. This includes implementing robust authentication and authorization mechanisms, encryption techniques, and role-based access controls.
3. Data Integration – the process of combining data from different sources and systems to create a unified and consistent view of data. It involves data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes, as well as the implementation of data integration technologies and platforms.
4. Master Data Management – organizes, centralizes, and transforms data from various sources to enhance data quality and enable informed decision-making. It facilitates uniformity and supports analytics by serving as a reliable reference for employees.
5. Data Architecture – designing the overall structure and organization of data within an organization. It includes defining data models, data flows, data storage, and data integration strategies to ensure data is organized and accessible.
6. Metadata Management – It involves capturing, organizing, and maintaining metadata, which provides information about the characteristics, context, and usage of data.
It includes creating data dictionaries, data catalogs, and metadata repositories to support data discovery, data lineage, and data governance.
Now we have established the foundation of an enterprise data management system, now the question is:
Before determining the stage of data management, firstly it's essential to understand the framework.
The data Maturity Curve is a framework that represents the stages of an organization's journey toward achieving data maturity. Roadmap for organizations to assess their current state of data management and identify areas for improvement.
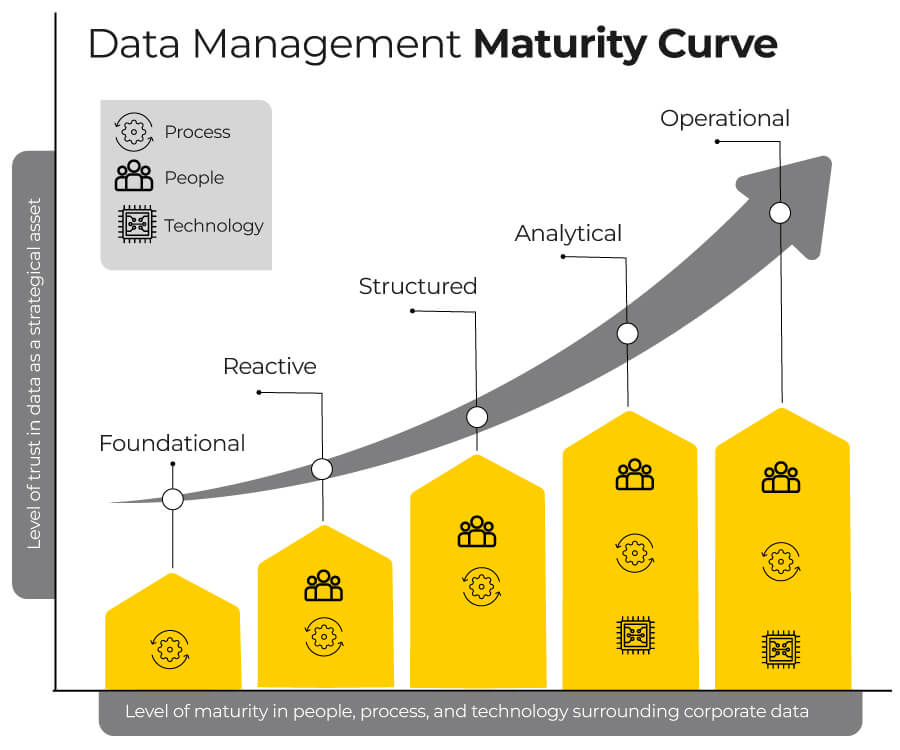
1. Foundational: In this stage, organizations recognize the importance of data management and begin laying the foundation. Data is stored in disparate systems, with limited integration and inconsistent processes. The focus is on understanding data sources and establishing basic data governance principles.
2. Reactive: Organizations address data challenges as they arise, such as data quality issues, data duplication, or data silos. Efforts are made to resolve immediate issues, but data management practices are still largely reactive. Data governance frameworks start to take shape, and awareness of data's value increases.
3. Structured: Organizations proactively establish data governance frameworks, policies, and standards. Data management processes are formalized, including data quality management, data integration, and data security. The emphasis is on establishing data management roles, responsibilities, and workflows.
4. Analytical: Organizations leverage advanced technologies and analytics to derive insights from their data. Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and data visualization tools are utilized to analyze and interpret data for informed decision-making. Data becomes a strategic asset, and data-driven initiatives drive business outcomes.
5. Optimized: In this final stage, data management practices are fully optimized. Organizations continuously refine their data governance strategies and processes. Data is seen as a critical asset, and a data-centric culture permeates the entire organization. Data-driven decision-making is embedded in all levels, driving innovation and strategic planning.
These refined pointers highlight the progressive nature of data maturity, from establishing foundations to achieving optimized data management practices. Organizations can use this framework to assess their current data management state and guide their journey toward higher data maturity and value extraction.
Considering all these components and maturity curves, formulating an enterprise data management strategy becomes feasible. Here are some best practices to keep in mind.
1. Assess Current Situation: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the current data management practices within your organization. Evaluate existing systems, processes, and data sources to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. This assessment will help inform the development of the enterprise data management strategy.
2. Define Needs and Objectives: Identify the specific needs and objectives of your organization related to data management. Understand the business drivers and desired outcomes to establish clear goals for the effective data strategy.
3. Identify the Needed Tools: Assess the tools and technologies required to support the EDM strategy. This may include data integration platforms, data quality tools, data governance software, analytics tools, and other data management solutions. Identify the tools that align with your objectives and fit the specific needs of your organization.
4. Implement Data Management Solutions: Based on the identified needs and objectives, implement data management solutions that align with your enterprise data management strategy. This may involve implementing data governance frameworks, data quality management processes, data integration mechanisms, and other relevant solutions to address the identified gaps.
5. Determine Standards, Policies, and Procedures: Define data standards, policies, and procedures that will govern data management practices. Establish guidelines for data quality, data governance, data security, data integration, and other relevant areas to ensure consistency and compliance.
6. Educate and Inform Stakeholders: Educate and inform stakeholders across the organization about the importance of effective data management and the benefits of the enterprise data strategy. Provide training programs, workshops, and communication channels to enhance data literacy and create awareness about EDM initiatives.
7. Emphasize Quality: Place a strong emphasis on data quality throughout the enterprise data management strategy. Implement data quality management processes, data profiling techniques, data cleansing activities, and regular data audits to ensure the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of the data.
8. Invest in the Right People and Technology: Ensure you have the right personnel with the necessary skills and expertise to drive the EDM data strategy. Invest in hiring or training data management professionals who can effectively implement and manage EDM initiatives. Additionally, invest in the appropriate technologies and tools that support your EDM goals.
Enterprise Management Software supports essential business processes by managing information flow, generating various reports, and enabling data analytics. This results in easier business planning, improved productivity, greater flexibility, and better record-keeping for compliance purposes.
Embrace uncertainty with confidence by mastering the art of enterprise data management.
Book a Discovery SessionAn efficient Enterprise Management Software system serves as a central hub for monitoring and managing complex organizational operations. It encompasses the following functions:
Bravo! You’ve made it till here. Now you have a fair understanding of enterprise data management.
At Polestar Analytics, we provide organizations with cutting-edge data management services and data engineering solutions by considering their existing business, data, and technology stack such as their data architecture, digital maturity, and hosting environment.
Still not aware of how business data holds key insights to solve complex business problems?
Time to unlock the true potential of Enterprise Data Management to drive meaningful insights for your business. Book consultation now
About Author

Marketing Consultant
Data Alchemy can give decision making the golden touch.