
Sign up to receive latest insights & updates in technology, AI & data analytics, data science, & innovations from Polestar Analytics.
Albert Einstein famously used thought experiments to visualize untested theories’ implications in the physical world. Similarly, business leaders need to visualize the multiple uses and implications of their data usage. This would help them understand the current situation based on past and present data to explore more avenues for the future. Today let’s explore in detail the true value of data and how to realize it for competitive advantage and building new revenue streams.
Gartner defines Data Monetization as “the process of using data to obtain quantifiable economic benefit”. Companies are always looking to expand their product offerings and services to bring in new sources of revenue every day, even data is not an exception. With the amount of data that is being generated and also the number of resources being leveraged to store and transform the data it is natural that companies look to gain more out of it.
Based on how the data is being used there are two main types of data monetization. The first and most direct method is data sharing with external and third-party sources i.e. direct sale of data or information bartering. The data can be in raw format or data that is already analyzed. One word of caution is to keep track of the data-sharing norms of their own location before doing the same.
The second method of data monetization which is safer from a legal point of view and gives the possibility of multiplication in the future is the indirect method i.e. using data to make business performance improvements and improve decision-making. Though many people call data the new oil or any commodity, one key feature that they forget about data is its consumption, data can be consumed more than once and its value. The value of data is not clear to most people initially and is dependent on how it is used.
In this indirect type of data monetization, the truly interesting concept is to find out the value of this data. This can be done by finding sources of optimization or bringing data-driven business models, for which there are many data analytics, business intelligence, EPM resources, and technologies that can help you. In this article, we would be mainly talking about the Indirect method of Data monetization.
According to a study by Kearney, “8 percent of companies that are market leaders in analytics have generated 60 percent more profit than the businesses that lag so far behind them”. The obvious but not-so-obvious benefit of data monetization through the indirect method is to improve the top and bottom lines of business.
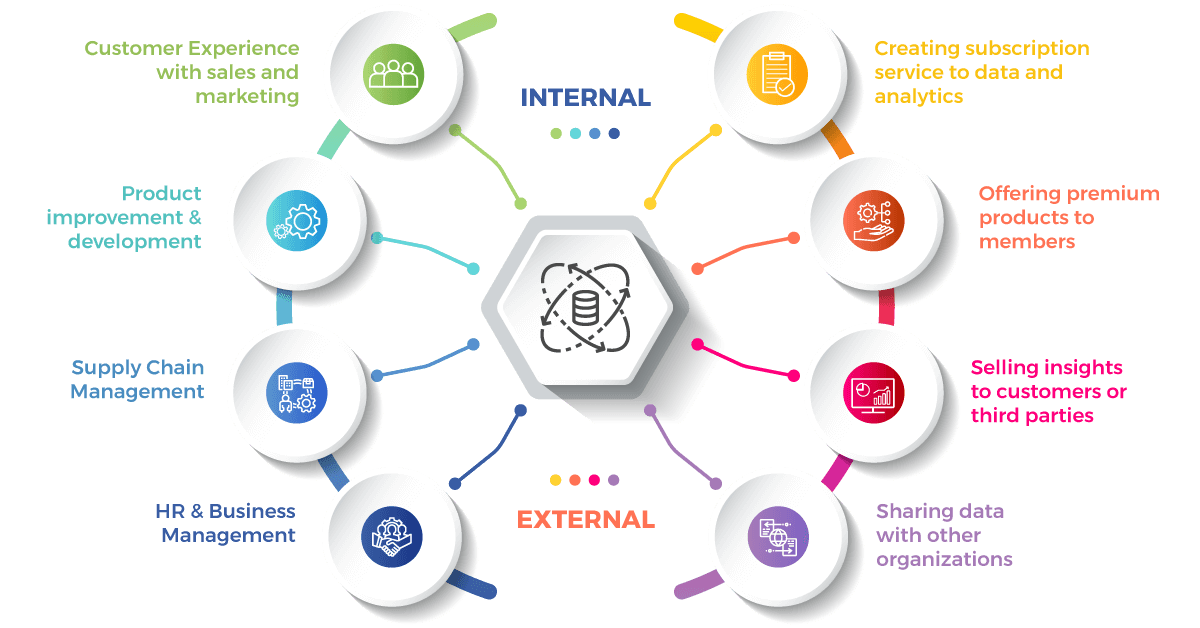
Some of the benefits and advantages of using Data Monetization include:
There is a need to change the POV of how companies view data from cost centers to profit centers. With data, there is a lot that can be unfolded once you put the time, investment, and resources into it. Different keys as the foundation of data monetization are
Data Management: Though this sounds obvious many organizations lack this step. They fail to identify the kind of data they need to capture and also lack capturing data with quality.
Data Strategy: As with any implementation, even data analytics or advanced analytics implementation would need a strategy in place to identify the BUs or the KPIs which would be needed to capture.
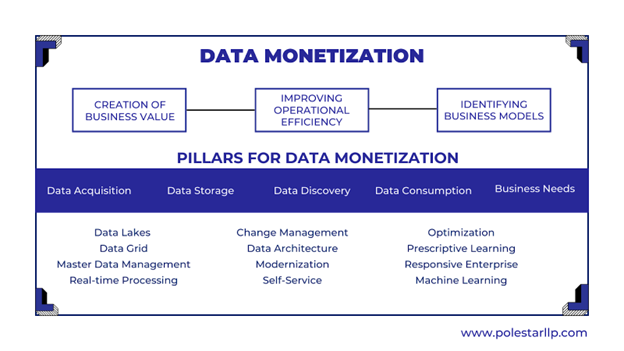
Data Analytics: Given that we intend to identify more opportunities from the internal data, having the required technical knowledge to do the same with analytics is needed. For making the understanding easy, we can divide this into broadly three spaces: Creation of business value, Improving Operational efficiency, and Identification of Business Models.
Creation of business value can be referred to as the processes in which you enable a seamless data platform that understands the current business scenario using historical data to create insights. Improving Operational Efficiency can be done by improving real-time insights to build efficient and agile manufacturing and logistics processes.
The last step of identifying business models can be done through data science and algorithm-driven data analytics to renew or build new revenue streams with scenario planning and analysis.
Though there are multiple ways to talk about data monetization, let’s take a look at the ways in which data analytics are useful. We have spoken about the broad use cases above where data analytics can be leveraged, but now let’s take a different perspective, and look at it from an organizational level.
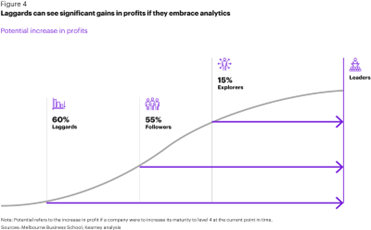
But before we go into the methods of data monetization, let’s take a look at how data analytics would be beneficial in terms of monetization. You might have seen this before or have heard of Analytics maturity stages by Kearney. The four stages include Laggards, Followers, Explorers, and Leaders. This analysis talks about how laggards experience 60% lesser profits than leaders, and only once you reach the explorers' stage can you see the true value of analytics.
So the next time you think about whether data analytics would be beneficial or not, or if you are not seeing results immediately think about which position you would have in the analytics maturity assessment, and how data analytics would be beneficial for your organization.
Insights as a service
This is about breaking down the data to the insight level i.e. transforming, analyzing, and drilling the data down to an insight level that can be shared with the business stakeholders or end users. This can be taken in a one-time or subscription format. Some of the examples include how companies like Meta or review platforms take subscriptions for insights about how customers interact with their platforms. This can help marketing or sales understand how to reach customers better. This can also be the creation of insights from the internal data by using data analytics or machine learning techniques.
Embedded Analytics
Though this can also be a part of Insights, it is important to note that with Embedded analytics you bring insights to existing workflows or existing applications by embedding visualizations or new dashboards in them. This is extremely useful when people are concerned with change management as one of the barriers i.e. change in the workflows or the need for learning new technologies as part of getting insights.
Data as a service
The most direct form of data analytics is data as a service. Not to be confused with Data analytics as a service, Data-as-a-service is all about selling data to consumers or intermediaries. The data can be in the form of raw data or congregated form. The data being sold can be without any insights or just graded data. For example, any data you gather from multiple sources by grading them about specific vendors, etc. also falls under this category. Such data can be shared via APIs, under online marketplaces, or direct data dumps.
Some people also add analytics-enabled platforms and business intelligence to this list. But I think that the three ways i.e. Insights as a service, Data as a service, and embedded analytics have some parts of platforms and BI to them.
Data Analytics & Data monetization has become a differentiator for most companies to help them understand and access newer sources of revenue. Though most organizations understand it, the concept is fairly new, according to a report by Mckinsey, “41 percent of respondents whose companies have begun to monetize data, a majority say they began doing so just in the past two years”
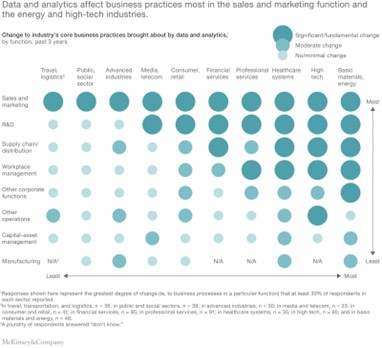
Some of the industries in which data monetization is rather prevalent now are materials and energy, financial services, and high-tech. The respondents at the high-performing companies which have implemented data monetization see a top-line benefit i.e. they are 3x more likely than others to say that their data monetization efforts contribute more than 20 percent to company revenues.
For example, let’s take a look at how Data Monetization would be beneficial for Manufacturing. Monetization of data in manufacturing results in increased productivity and sustainability. With data models of plant information, you can predict machine failures and schedule maintenance i.e. predictive maintenance. One can have more precise planning based on the geolocation of products and the demand, combine this with digital twin manufacturing, and you can have continuous quality control and potential realization.
One other example of this is the Mayo Clinic, which has announced a Clinical Data platform to use insights and knowledge extracted from data to improve healthcare and accelerate new treatments.
Now that we know of the multiple methods and the multiple benefits of data monetization let us also understand what the current barriers are:
When data is accessed in siloes or unnecessary data is captured by companies, it forms a barrier of resistance that can neither be leveraged nor utilized. Therefore, data management is a key requirement for the entire data monetization process.
You can understand the key elements of a winning data strategy in the infographic below:
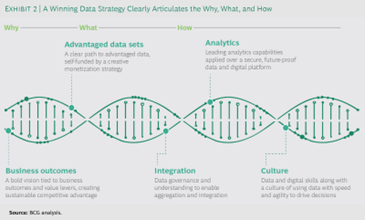
Source: BCG Analysis
Let it be moving from passive to active analytics or being more responsive data is at the heart of the operations. By monetizing your data, you can have access to scalable, agile, and flexible data analytics, which will in turn help your organization to adapt to new requirements and drive shorter times-to-insights.
With effective data monetization, you can get granular customization of functionality which would ensure performance regardless of the challenges ahead.
About Author

Data & BI Addict
When you theorize before data - Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts.