
Sign up to receive latest insights & updates in technology, AI & data analytics, data science, & innovations from Polestar Analytics.
Editor's Note: AI-powered banking data analytics is revolutionizing the way financial services firms manage operational risks. It's crucial for firms to tread carefully and evaluate the risks before implementing AI solutions. In this blog, we will explore the current state of AI and five key considerations that firms should keep in mind when incorporating AI into their operational risk management strategies.
Global Artificial Intelligence (AI) in banking had a market size of USD 8.30 billion in 2019 and is expected to reach USD 130 Billion by 2037 and register a CAGR of 42.9% during the forecast period.
A breakthrough technology, accelerating data availability, and the latest business models and value chains are revolutionizing the ways banks serve customers, operate internally, and interact with third parties. Operational risk must keep up with this spirited environment, involving the ongoing risk landscape.
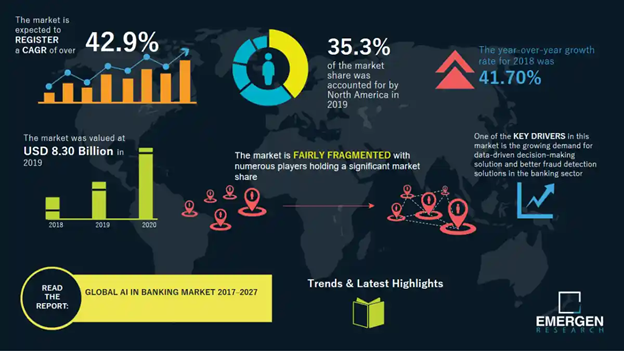
Source: Emergen
Legacy controls and processes must be updated, but banks can also look on the imperative to transform as an improvement opportunity. The adoption of latest technologies and the use of new data can improve operational risk management itself. The focus is on risk management, undertaken with greater efficiency and integrated with business decision-making.
Deploying advanced technologies is very significant in the present scenario for financial-services firms. And efforts to address the new complexities are bringing measurable bottom-line impact. For instance, one global bank tackled unacceptable false-positive rates in anti–money laundering (AML) detection—as high as 96%. Utilizing machine learning to identify critical data flaws, the bank made necessary data-quality enhancements and thereby quickly eliminated an estimated 35,000 investigative hours.
Furthermore, a North American bank assessed conduct-risk exposures in its retail sales force. Using banking analytics models to monitor behavioral patterns among 20,000 workers, the bank identified unwanted anomalies before they became tedious problems. The cases for change are diverse and compelling, but transformations can present formidable complexities for functions and their institutions.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is disrupting diverse industries, but banking is projected to benefit most from incorporating AI systems in the next couple of years. Analysts estimate that AI will save the banking industry more than $1 trillion by 2030.
The interest in adopting AI for risk management efforts is fueled by increasing data regulations and traditional methods of data oversight becoming unreliable, given the large volumes of data that organizations are handling. Amid these regulations and large volumes of data, organizations are desperate for resources to analyze, assess and monitor risk while staying current with compliance pressures.
Operational risks are one of the most significant types of risks faced by banks. These risks arise from the failure of people, processes, or systems in an organization, which can lead to financial loss, reputational damage, and regulatory sanctions. Operational risks can also arise from external events such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, or political instability.
In this blog, we will explore the key operational risks faced by banks and how they can be managed.
Therefore, AI has the potential to significantly reduce operational risks in the finance sector by automating processes, detecting anomalies, and identifying potential risks before they materialize. By leveraging the power of AI in banking, financial institutions can improve their cybersecurity, compliance, customer service, and risk management capabilities, and ultimately reduce the likelihood and impact of operational risks.
About Author

AI & EPM Head Top AI voice & Tedx Speaker
Data unveils impact, and with data, you can infuse a greater degree science to your decisions